Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 26 junho 2024

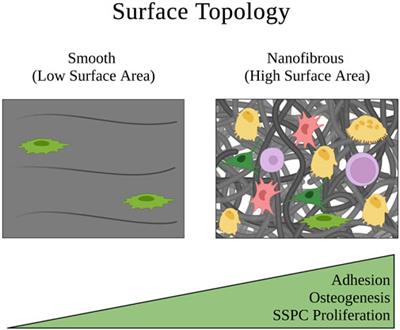
Frontiers Mechanobiology-informed biomaterial and tissue engineering strategies for influencing skeletal stem and progenitor cell fate
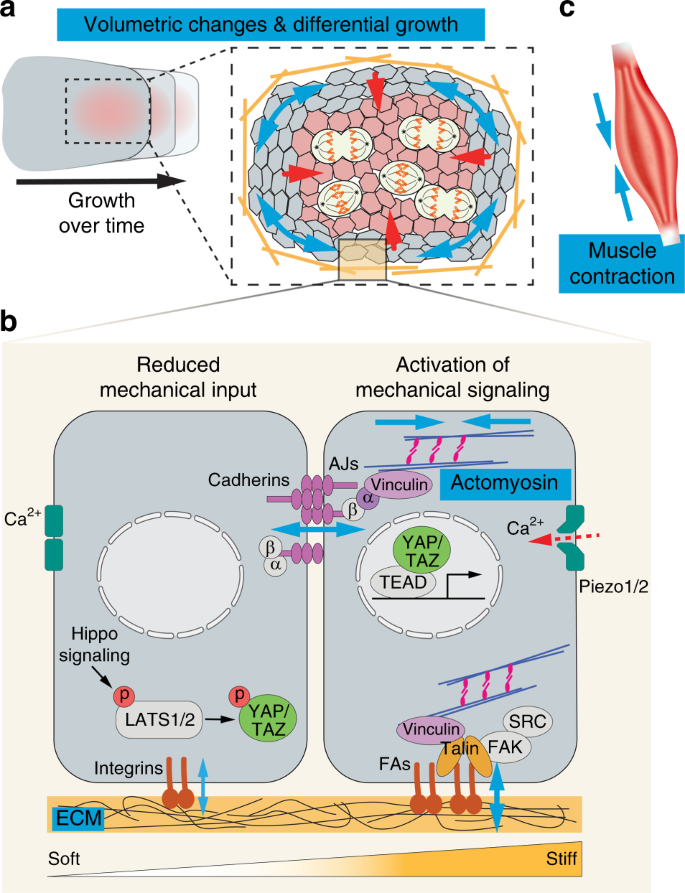
FACEts of mechanical regulation in the morphogenesis of craniofacial structures
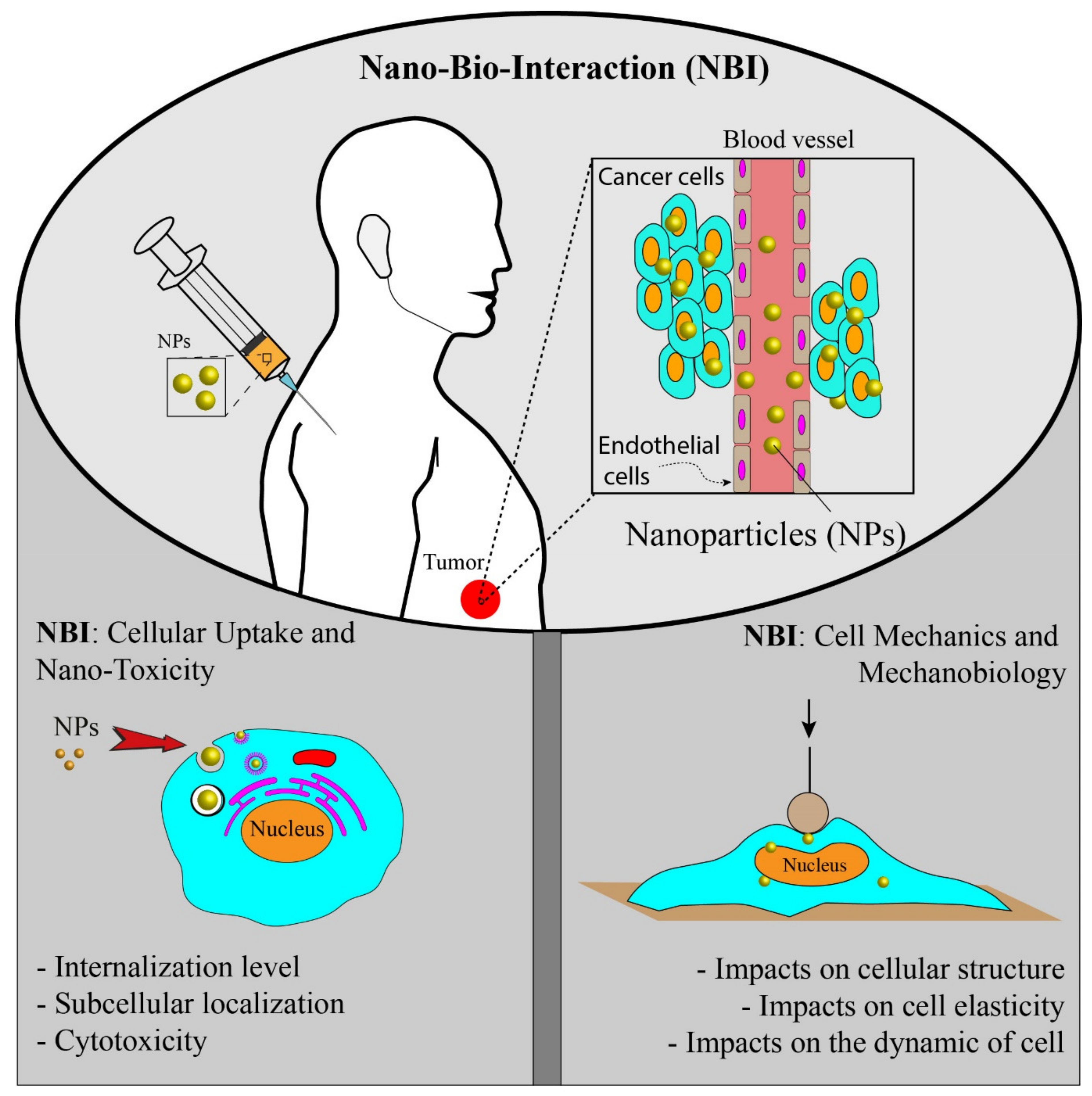
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Morphology as indicator of adaptive changes of model tissues in osmotically and chemically changing environments
PDF) Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface
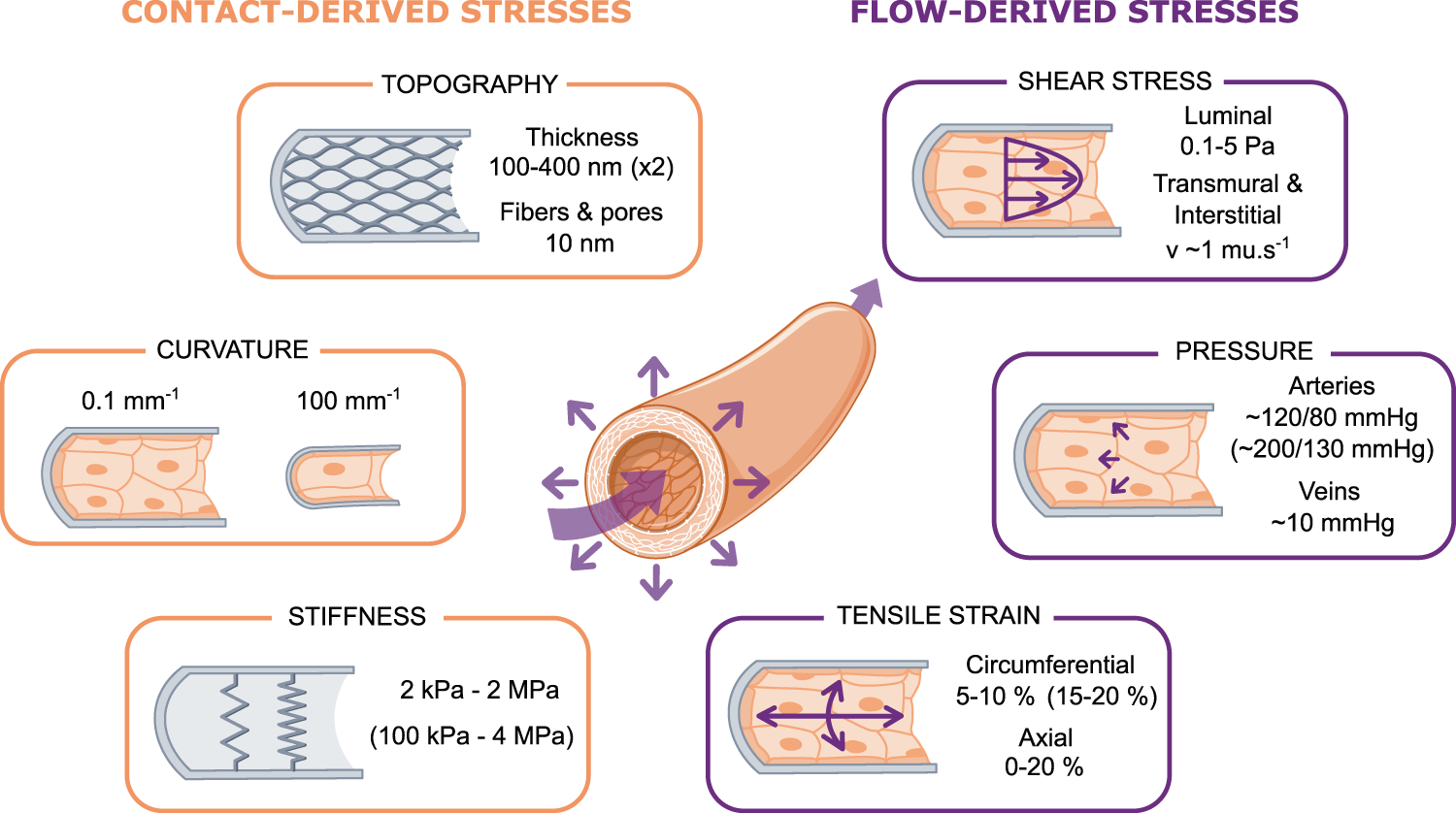
Integration of substrate- and flow-derived stresses in endothelial cell mechanobiology
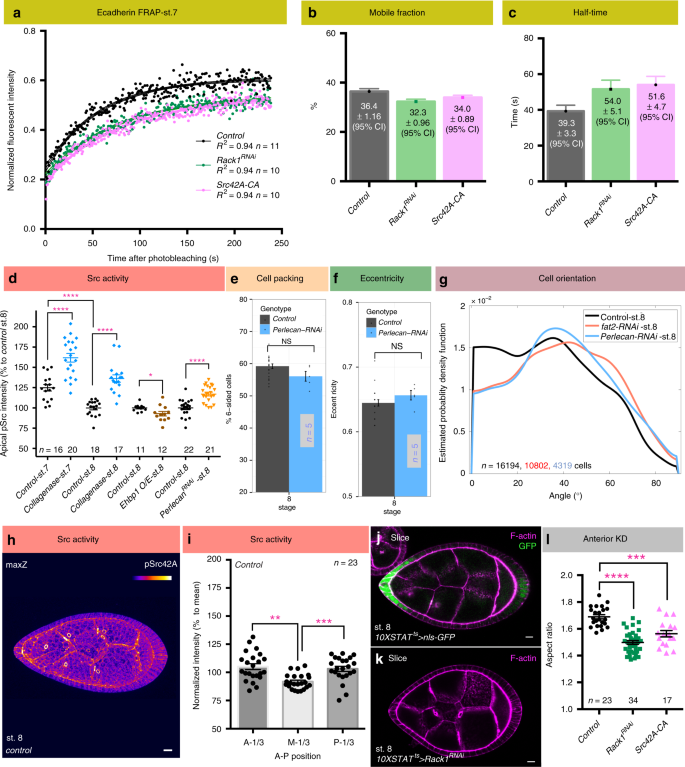
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation
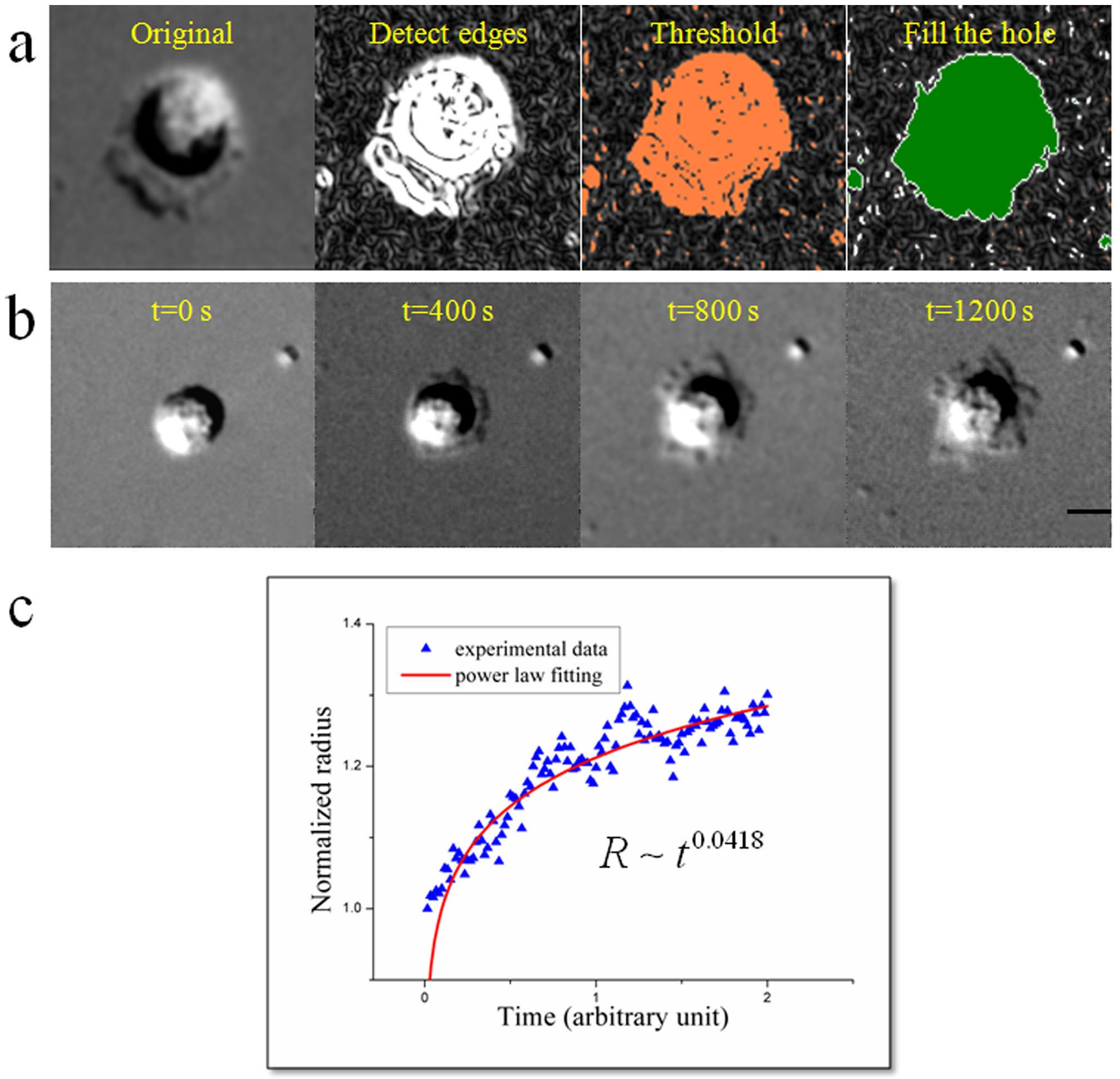
Kinetic behaviour of the cells touching substrate: the interfacial stiffness guides cell spreading
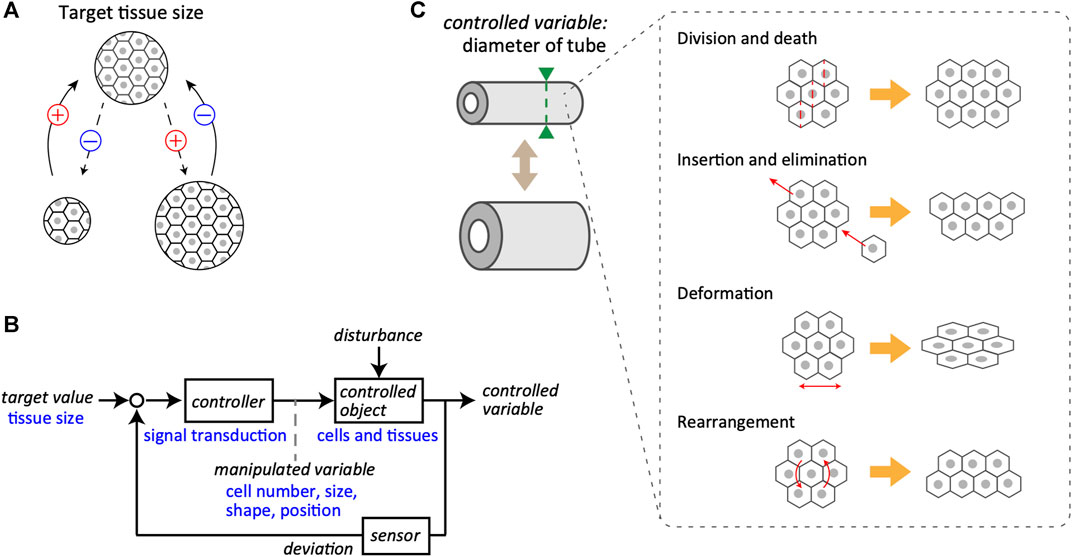
Frontiers Mechanical Feedback Control for Multicellular Tissue Size Maintenance: A Minireview

Cell Shape and Durotaxis Explained from Cell-Extracellular Matrix Forces and Focal Adhesion Dynamics - ScienceDirect
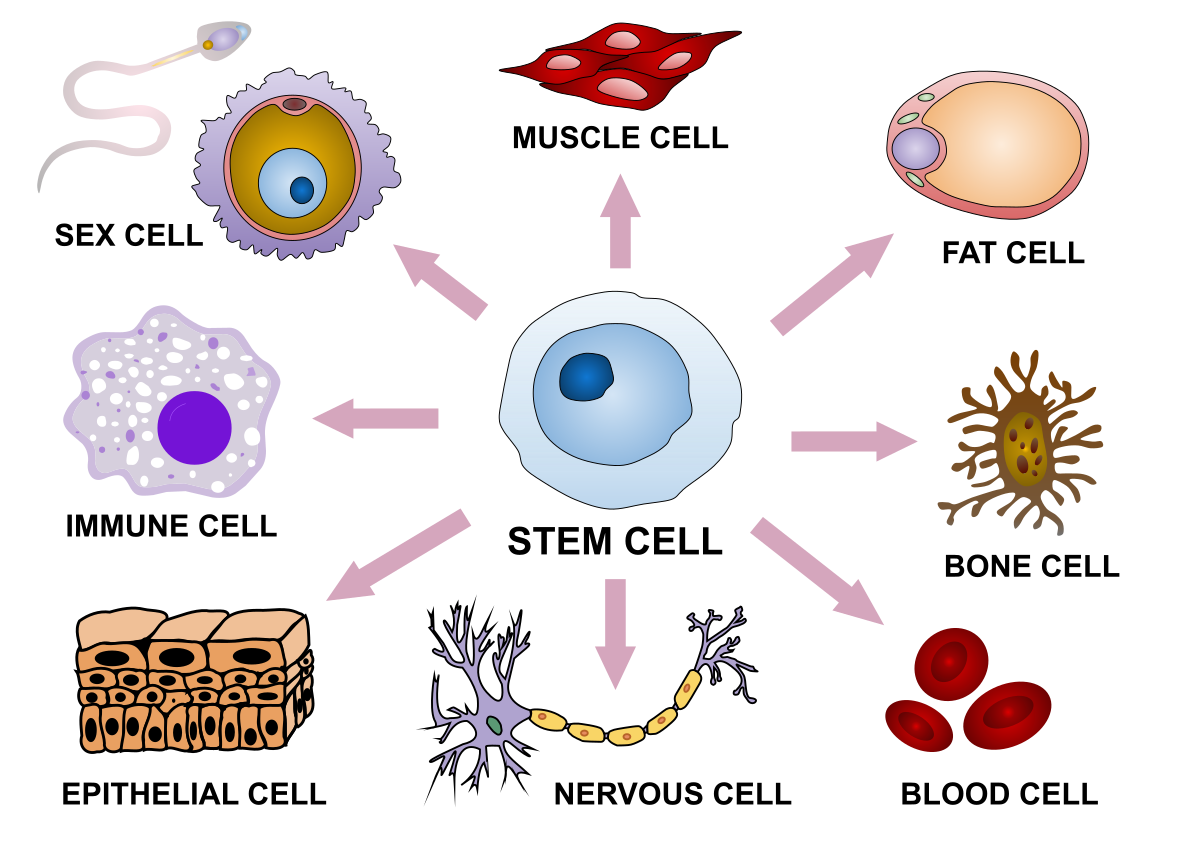
Cellular differentiation - Wikipedia
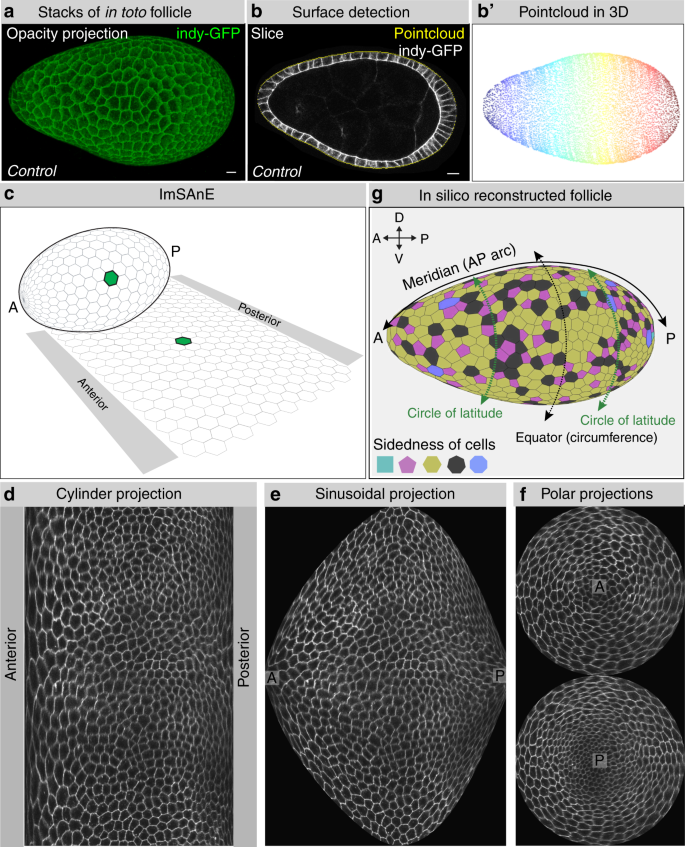
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation

Surface Roughness and Substrate Stiffness Synergize To Drive Cellular Mechanoresponse
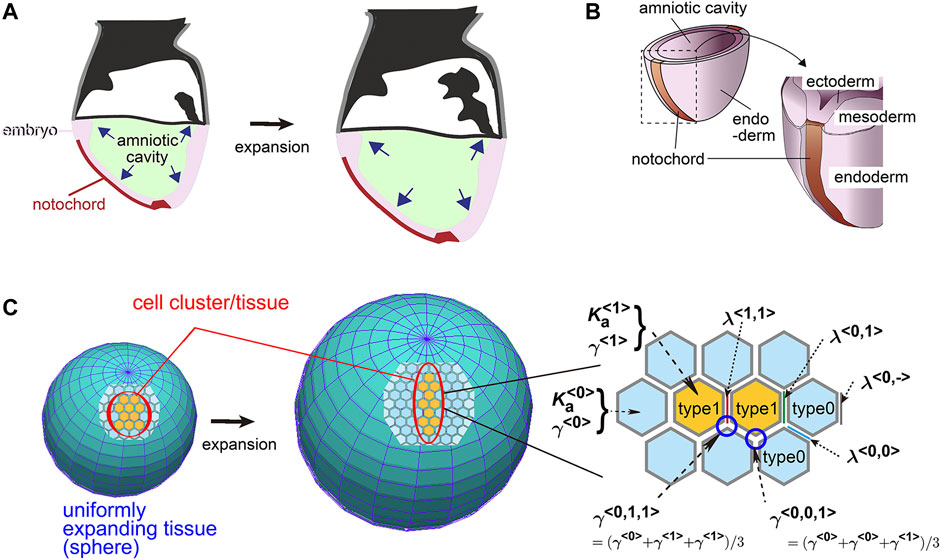
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

Comparison of tissue stiffness in different fixative conditions. (A)
Recomendado para você
-
 Moneybagg Yo - U Played feat. Lil Baby (Official Audio)26 junho 2024
Moneybagg Yo - U Played feat. Lil Baby (Official Audio)26 junho 2024 -
 Worlds - IdleOn MMO Wiki26 junho 2024
Worlds - IdleOn MMO Wiki26 junho 2024 -
 The Commodordion26 junho 2024
The Commodordion26 junho 2024 -
The cosy autumnal crossword26 junho 2024
-
 YupYay 4 Pack Custom OEM R4 Keycaps PBT Mechanical Keyboard Keycaps Cute Cat Paw Key Cap Kawaii Gaming Keycaps for Mechanical Keyboard with Keycap Puller (White Base) : Electronics26 junho 2024
YupYay 4 Pack Custom OEM R4 Keycaps PBT Mechanical Keyboard Keycaps Cute Cat Paw Key Cap Kawaii Gaming Keycaps for Mechanical Keyboard with Keycap Puller (White Base) : Electronics26 junho 2024 -
 Pin on All Things Crochet! Crochet Patterns, techniques, inspiration and more!26 junho 2024
Pin on All Things Crochet! Crochet Patterns, techniques, inspiration and more!26 junho 2024 -
 Japan Disney Store Mickey Mouse Stuffed Plush Keychain Retro Modern Mascot Charm26 junho 2024
Japan Disney Store Mickey Mouse Stuffed Plush Keychain Retro Modern Mascot Charm26 junho 2024 -
 Razer Nostromo PC Gaming Keypad : Electronics26 junho 2024
Razer Nostromo PC Gaming Keypad : Electronics26 junho 2024 -
 Moneybagg Yo - U Played feat. Lil Baby (Slowed Down + Reverb)26 junho 2024
Moneybagg Yo - U Played feat. Lil Baby (Slowed Down + Reverb)26 junho 2024 -
 Blind Box Sanrio Capsule Squishy Series 3 - Steam Bun – Off the Wagon Shop26 junho 2024
Blind Box Sanrio Capsule Squishy Series 3 - Steam Bun – Off the Wagon Shop26 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 DEVIL MAY CRY 4 - VERGIL26 junho 2024
DEVIL MAY CRY 4 - VERGIL26 junho 2024 -
 Assistir Black Clover Dublado Episódio 49 » Anime TV Online26 junho 2024
Assistir Black Clover Dublado Episódio 49 » Anime TV Online26 junho 2024 -
 Melhor jogador do Mundo FIFA: quem leva o troféu? The Best FIFA26 junho 2024
Melhor jogador do Mundo FIFA: quem leva o troféu? The Best FIFA26 junho 2024 -
 The King of Fighters Lives On in China and Latin America26 junho 2024
The King of Fighters Lives On in China and Latin America26 junho 2024 -
backrooms level 94 animations|TikTok Search26 junho 2024
-
 The King of Fighters '97 Released 20 Years Ago26 junho 2024
The King of Fighters '97 Released 20 Years Ago26 junho 2024 -
 Endnight Games Reflects on Developing The Forest and Discusses What's Next : r/pcgaming26 junho 2024
Endnight Games Reflects on Developing The Forest and Discusses What's Next : r/pcgaming26 junho 2024 -
 Free STL file Gravestone cookie cutter RIP・3D print design to26 junho 2024
Free STL file Gravestone cookie cutter RIP・3D print design to26 junho 2024 -
 BOLIVIA X BRASIL AO VIVO COM IMAGENS - JOGO DE HOJE - ASSISTA26 junho 2024
BOLIVIA X BRASIL AO VIVO COM IMAGENS - JOGO DE HOJE - ASSISTA26 junho 2024 -
 Paradise and Hell : The Final Day in the Light of the Qur'an and Sunnah : Islamic Creed Series Volume 5 (2nd Edition)26 junho 2024
Paradise and Hell : The Final Day in the Light of the Qur'an and Sunnah : Islamic Creed Series Volume 5 (2nd Edition)26 junho 2024

